The global supply chain is a $50 trillion industry and is the foundation of our global economy. While information technology has improved the flow of goods globally over the last few decades, as the COVID-19 crisis revealed there is still critical work to do. Today’s supply chains are complex, with parties conducting their transactions through a Byzantine network of computer systems with disparate applications like e-mail, phone, and fax. There are invoices, letters of credit, bank guarantees, bills of lading, tax forms, receipts, and other paperwork moving through this complex labyrinth. Payments are made through a hodgepodge of intermediaries, and consumers and supply chain players alike struggle to get accurate information.



Web3 and Blockchain Transformations in Global Supply Chains
This course is part of Web3 and Blockchain in Global Commerce Specialization


Instructors: Don Tapscott
Sponsored by Barbados NTI
2,192 already enrolled
(27 reviews)
What you'll learn
The roles of key participants in the global trade network and where the needs of each participant align with the value characteristics of blockchain
What it means to "tokenize" an asset, and approaches to securing the physical-digital interface
Examples of sensor-based logistics, and IoT challenge areas that show promise for blockchain-based solutions
Blockchain solutions for provenance, traceability, ethical sourcing, and asset life-cycle management
Skills you'll gain
- Transportation, Supply Chain, and Logistics
- Emerging Technologies
- Content Management
- Logistics Management
- Supply Chain Systems
- Supply Chain Management
- Internet Of Things
- Blockchain
- Content Development and Management
- Logistics
- Digital Content
- Digital Assets
- Product Lifecycle Management
- Supply Chain
- Product Management
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
21 assignments
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills

Build your subject-matter expertise
- Learn new concepts from industry experts
- Gain a foundational understanding of a subject or tool
- Develop job-relevant skills with hands-on projects
- Earn a shareable career certificate


Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV
Share it on social media and in your performance review

There are 5 modules in this course
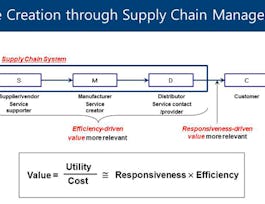
Global trade has grown in complexity and magnitude over millennia, but its processes remain relatively unchanged. This module explores how blockchain can help modernize global trade and link together other capabilities for the twenty-first century. In this module, you will learn how various participants in the global trade network stand to derive unique value from blockchain technology—including banks and financiers, corporations, freight forwarders and carriers, customs and port authorities, regulatory bodies, and insurance providers. You will explore the ways that blockchain serves to link together organizations, industries, and technologies, and fosters an approach to collaboration that will drive new efficiencies.
What's included
8 videos4 readings4 assignments1 discussion prompt
Most supply chains today still rely heavily on opaque, time-consuming, and costly processes. Documentation is largely paper-based and handled manually. Approvals from multiple parties at each checkpoint often cause delays and are susceptible to fraud on cross-border orders. Catching mistakes in compliance and quality control is difficult. In this module, you will learn how blockchain can help mitigate the complexity of global supply chains by building trustable digital relationships among partners, goods, and customers.
What's included
9 videos5 readings5 assignments
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolves around connectivity, identification, sensing, remote monitoring, and actuation of physical objects. In the context of global supply chains, the application of IoT to sensor-based logistics enables cargo data—such as location, temperature, humidity, pressure, shock, and light exposure—to be captured and transmitted to multiple parties, allowing them to improve overall visibility and respond to unexpected deviations. In this module, you will learn how blockchain can help achieve autonomous and contract-based communication between physical things, providing an auditable record for products in transit.
What's included
8 videos4 readings4 assignments
Provenance and traceability are vexing challenges for a wide range of companies and their supply chains. A supply chain represents all links between parties involved in creating and distributing goods, starting with suppliers of unprocessed raw materials and ending with the delivery of a finished product to the consumer. The application of blockchain for provenance in supply chains aims at providing deep-tier visibility into the origins of a product. In this module, you will learn how blockchain has the potential to provide unprecedented supply-chain visibility in near real time, serving to combat counterfeit goods, enable ethically-sourced materials, track food safety from farm to fork, and increase buyer trust.
What's included
7 videos4 readings3 assignments1 discussion prompt
Globalization and volatility in demand require an increasing degree of flexibility in the production of goods and equipment. Blockchain has the potential to redefine economic structures and value flows that underpin supply-chain decision-making. This module explores three opportunities for blockchain in reshaping—or perhaps reversing—-global trade. First, you will learn how blockchain enables new models for distributed manufacturing, facilitating interactions between buyers and manufacturers to streamline production processes. Second, you will explore blockchain’s role in securing end-to-end additive manufacturing (AM) processes, with smart contracts serving as a security layer underpinning AM transactions. Third, you will learn how blockchain facilitates asset life-cycle management, providing a shared and immutable product memory and trail of actionable data over an asset’s life cycle between multiple parties. The module concludes with a discussion of the enabling considerations for blockchain in global trade, including business considerations (e.g. governance, standards, regulations) and technology considerations (e.g. scalability, interoperability, and integration with legacy systems).
What's included
10 videos3 readings5 assignments
Instructors


Offered by
Why people choose Coursera for their career




Learner reviews
27 reviews
- 5 stars
78.57%
- 4 stars
17.85%
- 3 stars
0%
- 2 stars
0%
- 1 star
3.57%
Showing 3 of 27
Reviewed on May 8, 2023
The course was well designed, easy to understand , very informative and well delivered
Reviewed on Apr 23, 2023
An Excellent course and gives real life examples of implementation of Blockchain in Supply chains
Reviewed on Jul 4, 2023
It is a good course for people who is not in the blockchain area.
Recommended if you're interested in Business

Duke University
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology(KAIST)
University of California, Irvine

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 10,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy



