- Browse
- Database
Database Courses
Database courses can help you learn data modeling, SQL querying, database design, and data normalization. You can build skills in optimizing queries, managing transactions, and ensuring data integrity. Many courses introduce tools like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB, demonstrating how to implement these skills in real-world applications. You'll also explore concepts such as relational databases, NoSQL systems, and data warehousing, equipping you to handle various data management challenges effectively.
Popular Database Courses and Certifications

Skills you'll gain: Data Migration, Google Cloud Platform, PostgreSQL, Operational Databases, Data Validation, Data Integrity, Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
Beginner · Project · Less Than 2 Hours
 Status: Free TrialFree TrialJ
Status: Free TrialFree TrialJJohns Hopkins University
Skills you'll gain: Data Import/Export, Web Scraping, Tidyverse (R Package), Data Integration, Data Manipulation, Data Transformation, Relational Databases, Google Sheets, Unstructured Data, R Programming, Extensible Markup Language (XML), Spreadsheet Software, Databases, SQL, Application Programming Interface (API)
4.7·Rating, 4.7 out of 5 stars51 reviewsBeginner · Course · 1 - 3 Months
 Status: FreeFreeD
Status: FreeFreeDDeepLearning.AI
Skills you'll gain: LLM Application, Tool Calling, AI Workflows, Hugging Face, Unstructured Data, SQL, Web Services, Prompt Engineering, AI Enablement, Database Management, Restful API, Data Processing
4.5·Rating, 4.5 out of 5 stars28 reviewsIntermediate · Project · Less Than 2 Hours
 Status: Free TrialFree TrialU
Status: Free TrialFree TrialUUniversity of Colorado Boulder
Skills you'll gain: Computational Logic, Mathematical Modeling, System Requirements, Functional Requirement, Theoretical Computer Science, Verification And Validation, Control Systems, Network Model, Systems Analysis, Automation, Mechanical Engineering, Real-Time Operating Systems, Agentic systems, Differential Equations, Safety Assurance, Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, Linear Algebra, Algorithms, Applied Mathematics
Build toward a degree
3.6·Rating, 3.6 out of 5 stars35 reviewsIntermediate · Specialization · 3 - 6 Months
 Status: PreviewPreview
Status: PreviewPreviewSkills you'll gain: MySQL, Business Intelligence, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), SQL, Relational Databases, Data Presentation, Data Visualization Software, Database Management, Databases, Data Access, Query Languages, Data Transformation, Performance Tuning
4·Rating, 4 out of 5 stars31 reviewsBeginner · Course · 1 - 4 Weeks
 C
CCoursera
Skills you'll gain: PostgreSQL, SQL, Query Languages, Data Transformation, Data Manipulation, Database Development, Data Management
4.5·Rating, 4.5 out of 5 stars31 reviewsAdvanced · Guided Project · Less Than 2 Hours
 Status: Free TrialFree TrialU
Status: Free TrialFree TrialUUniversity of Colorado Boulder
Skills you'll gain: Performance Testing, Scalability, Data Architecture, Software Architecture, Distributed Computing, Predictive Modeling, Performance Tuning, Microservices, Big Data, Software Engineering, Database Systems, Data Store, Model Evaluation
Build toward a degree
3.5·Rating, 3.5 out of 5 stars31 reviewsAdvanced · Course · 1 - 4 Weeks
 Status: Free TrialFree TrialV
Status: Free TrialFree TrialVVanderbilt University
Skills you'll gain: Spring Boot, Spring Framework, Restful API, Application Programming Interface (API), API Design, Data Persistence, Web Applications, Application Frameworks, Software Testing, Object-Relational Mapping, Hibernate (Java), Application Security, Authentications, JSON, Authorization (Computing), Dependency Analysis
4.2·Rating, 4.2 out of 5 stars29 reviewsBeginner · Course · 1 - 4 Weeks
 Status: Free TrialFree TrialU
Status: Free TrialFree TrialUUniversità di Napoli Federico II
Skills you'll gain: NoSQL, Apache Hadoop, Apache Hive, Big Data, Database Systems, Artificial Intelligence, Databases, Distributed Computing, Data Processing, Scalability, Business Intelligence, Data Management
4.1·Rating, 4.1 out of 5 stars26 reviewsBeginner · Course · 1 - 4 Weeks
 Status: NewNewStatus: PreviewPreviewV
Status: NewNewStatus: PreviewPreviewVVanderbilt University
Skills you'll gain: Model Context Protocol, Generative AI Agents, AI Enablement, Email Automation, Business Process Automation, Generative AI, AI Product Strategy, Agentic systems, Initiative and Leadership, Tool Calling, Anthropic Claude, ChatGPT, Automation, Responsible AI, Marketing Automation, Business Solutions, Multimodal Prompts, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML), Prompt Engineering, IT Automation
4.3·Rating, 4.3 out of 5 stars25 reviewsBeginner · Course · 1 - 4 Weeks
 Status: Free TrialFree Trial
Status: Free TrialFree TrialSkills you'll gain: Information Privacy, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Personally Identifiable Information, Data Security, Data Governance, Data Ethics, Data Loss Prevention, Security Controls, Regulatory Compliance, Compliance Management, Compliance Training, Data Integrity, Security Strategy, Regulatory Requirements, Employee Training
4.8·Rating, 4.8 out of 5 stars36 reviewsBeginner · Course · 1 - 4 Weeks

Skills you'll gain: SQL, Query Languages, Database Design, Performance Tuning, Database Management, Database Development, Databases, PostgreSQL, Data Access
3.2·Rating, 3.2 out of 5 stars32 reviewsIntermediate · Guided Project · Less Than 2 Hours
In summary, here are 10 of our most popular database courses
- Migrating to AlloyDB from PostgreSQL Using Database Migration Service: Google Cloud
- Importing Data in the Tidyverse: Johns Hopkins University
- Function-Calling and Data Extraction with LLMs: DeepLearning.AI
- Foundations of Autonomous Systems: University of Colorado Boulder
- MySQL for Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: Edureka
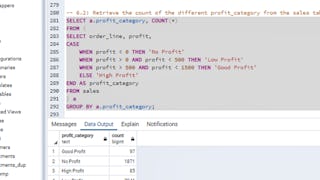
- SQL CASE Statements: Coursera
- Software Architecture Patterns for Big Data: University of Colorado Boulder
- Building HTTP APIs with Spring: Vanderbilt University
- A quick tour on Big Data and Business Intelligence: Università di Napoli Federico II
- Model Context Protocol for Leaders: Generative AI Agents: Vanderbilt University










